Flow Measurement in Subsea Applications
Subsea flow measurement typically refers to instruments tasked with performing one of several primary functions in hydrocarbon extraction arrays on the sea floor. These are chiefly used to monitor the flow of extracted products like natural gas and crude oils, or for measuring and metering chemical additives into flow lines via injection systems. They are also crucial in the manufacture of underwater Blowout Preventers (BOPs) and Remote Operated Vehicles (ROVs).
The challenges posed for subsea flow measurement are varied and significant. Instruments must perform under extreme pressures and low temperatures, without succumbing to the constant wearing forces of tidal erosion. The corrosiveness of seawater can also be an important factor for consideration. Oxidation and galvanic corrosion are constant concerns for subsea flow measurement instruments, as they are typically engineered from high-strength alloys that may be susceptible to pitting corrosion or the formation of biofilms.
This blog post will explore some of the most common subsea applications of flow measurement instruments, and how AW-Lake products have risen to the inherent challenges of demanding marine industries.
Subsea Chemical Injection
Chemical injection refers to the addition of various chemical additives directly into the flow stream connecting a subsea well to an offshore facility. These biocides, diluents, inhibitors, and various agents facilitate high yield flows with low particulate accumulation.
While the chemical containers are typically located topside on the petrochemical platform, the injection system can be positioned close to the subsea well. Flow measurement instruments are placed in proximity to the injector, due to the differential flow behavior of chemicals under different temperature and pressure values.
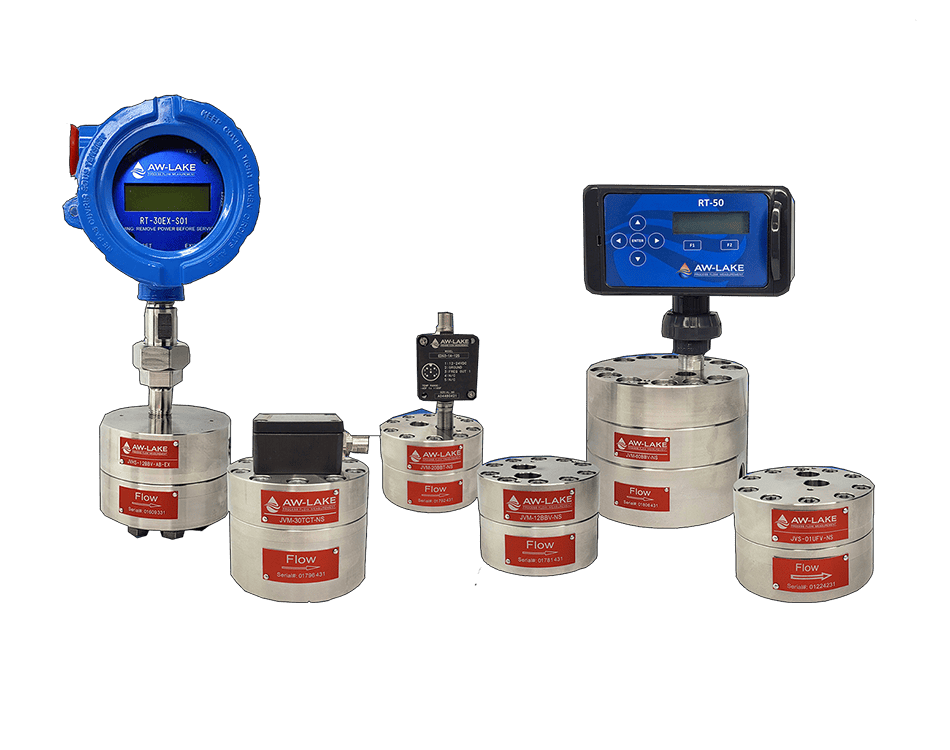
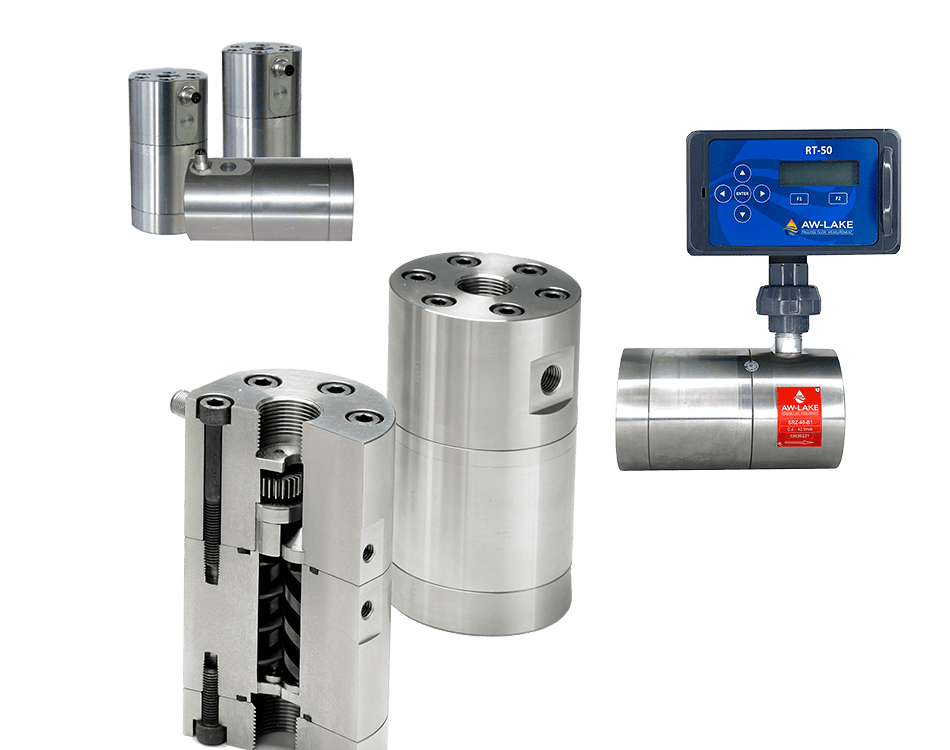
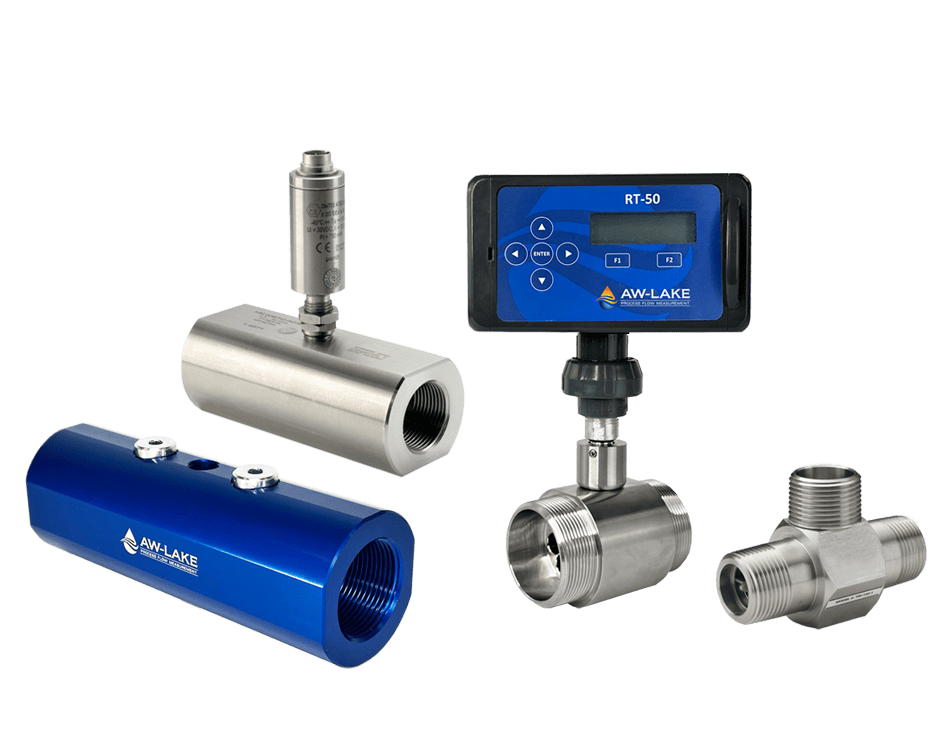
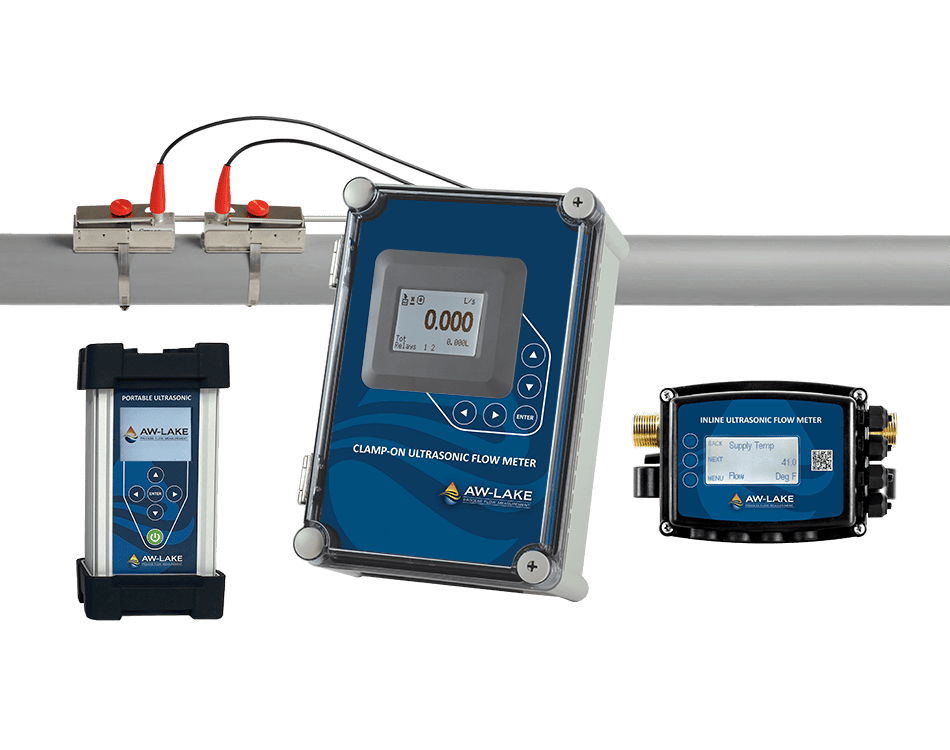
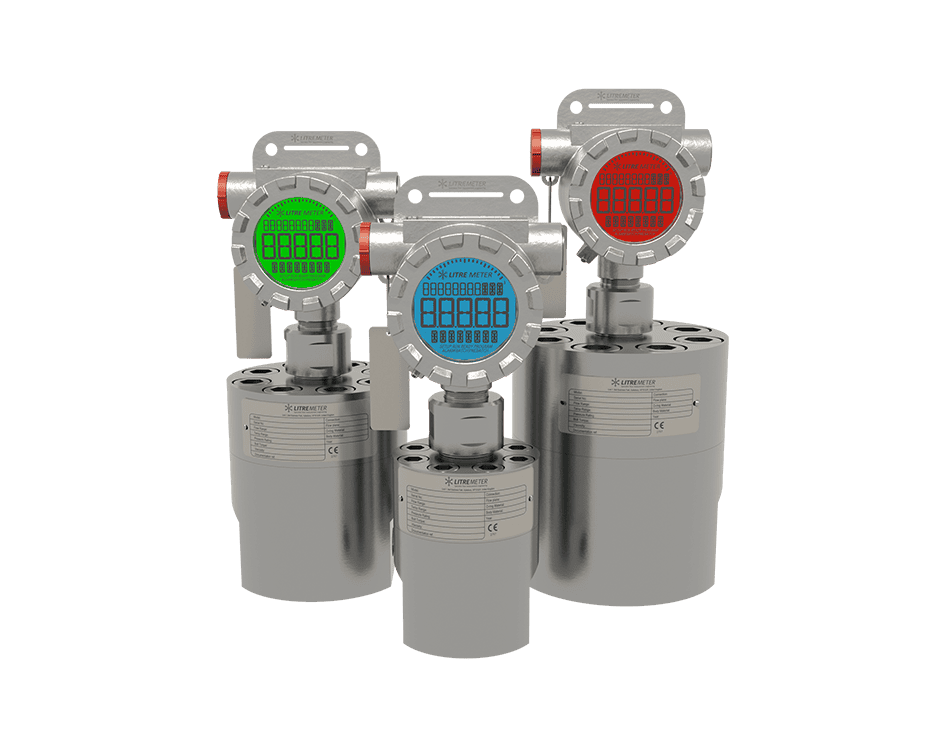
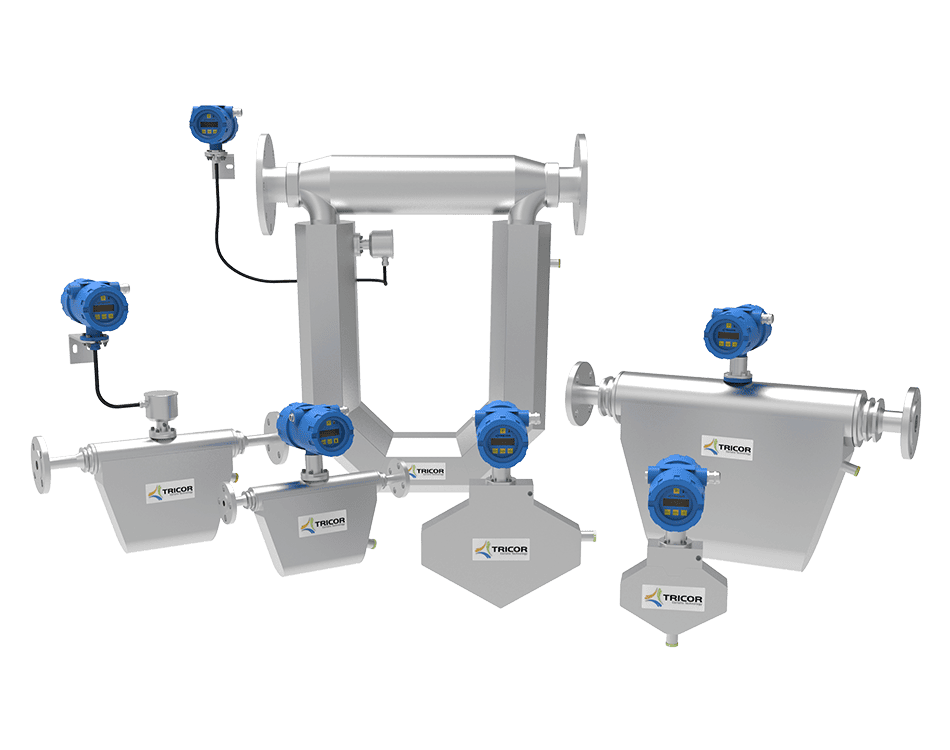
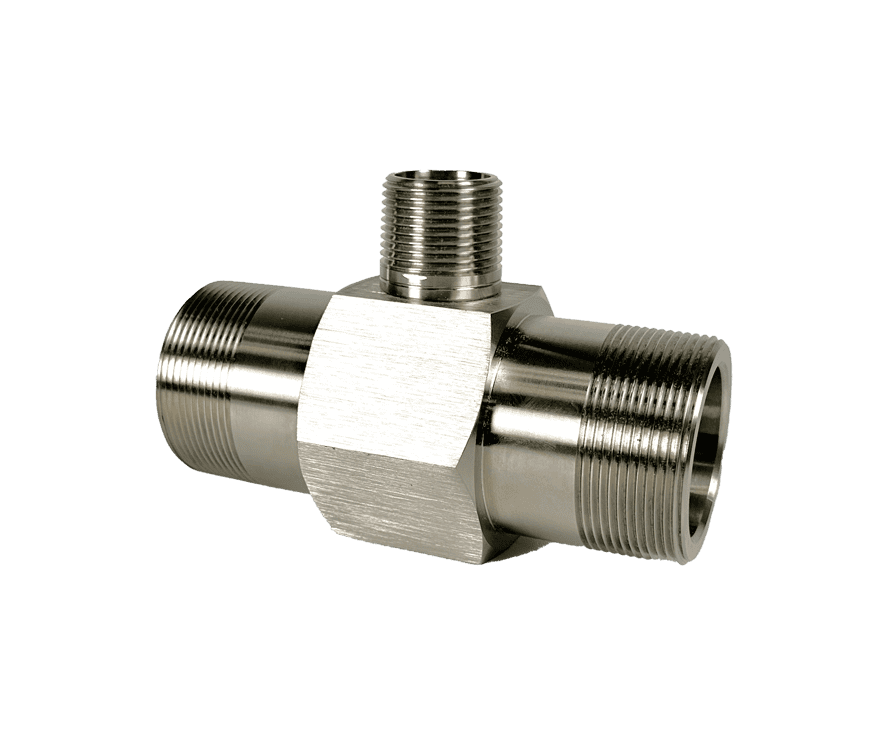
AW-Lake Subsea Positive Displacement (PD) and turbine flow meters are advanced flow measurement solutions for subsea chemical injection systems. They are housed in corrosion-resistant bodies of either stainless steel or titanium, providing suitable resistance to chlorination in normal salinity seawater. PD and turbine flow meters are operable at depths of 10,000 feet and able to withstand internal pressures of 15,000 psi.
Read more about flow measurement for chemical injection with our previous blog post: Chemical Measurement for High and Low-Pressure Injection.
Flow Measurement for ROVs
Subsea maintenance is routinely carried out using ROVs, which utilize a host of hydraulic systems to perform inspection and recovery of equipment on the ocean floor. Flow measurement systems are located onboard the ROV to closely monitor hydraulic fluids in the manipulator arms and propulsion system.
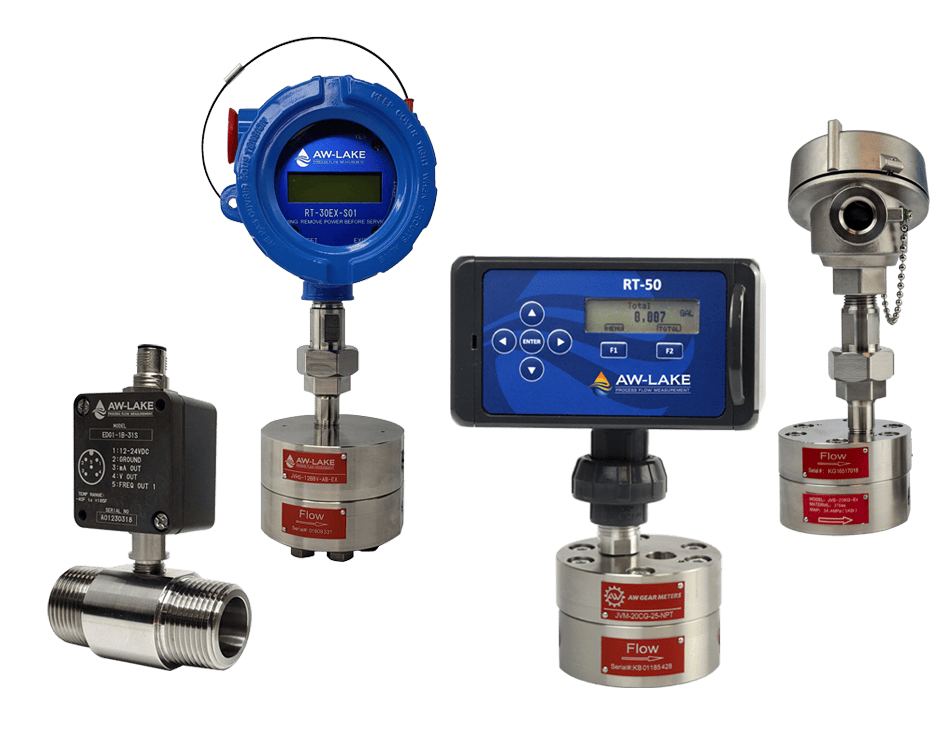
AW-Lake Turbine Flow Meters are ideal for monitoring the flow of hydraulic fluids at working pressures of up to 20,000 psi, enabling accurate in situ monitoring of low viscosity liquids.
Blowout Preventers
Subsea BOPs are specialized valves used to seal and monitor hydrocarbon wells to prevent blowout events. The uncontrolled release of pressure or hydrocarbon flows can pose a safety issue for offshore facilities, including the potential for environmentally hazardous oil spills. BOPs are now widely installed to offshore oil stacks as a preliminary safety measure to avoid catastrophic equipment failure.
AW-Lake’s Positive Displacement and Turbine Flow Meters are also able to perform hydraulic fluid monitoring for BOP systems, with operable temperature as low as -40°C and a wide flow range.
Subsea Measurement with AW-Lake
AW-Lake specializes in flow measurement for demanding areas of application. We provide a range of flow meters suitable for application in hard-wearing and corrosive environments, ensuring optimal operating conditions are maintained throughout production.
If you would like any more information about our flow measurement solutions, please do not hesitate to contact us directly.
Stay Up to Date With Everything AW-Lake





TASI Measurement Modernizes Brand to Match Innovation in Instrumentation